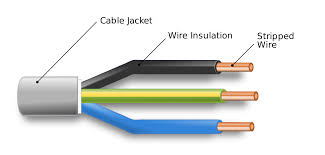
Cable conductors and their insulation property
Cable conductors
For all the conductor was, at one time, almost universally stranded copper but because of scarcity of copper, only aluminum is allowed to be used in power cables in India. Copper conductor is only used for cable used in control circuit.
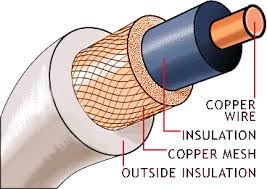 The stranding is necessary to provide flexibility to cables and the conductor numbers are 3, 7,9,37, and so on, all numbers except 3 having a centrally disposed conductor with the other around it.
The stranding is necessary to provide flexibility to cables and the conductor numbers are 3, 7,9,37, and so on, all numbers except 3 having a centrally disposed conductor with the other around it.
 The stranding is necessary to provide flexibility to cables and the conductor numbers are 3, 7,9,37, and so on, all numbers except 3 having a centrally disposed conductor with the other around it.
The stranding is necessary to provide flexibility to cables and the conductor numbers are 3, 7,9,37, and so on, all numbers except 3 having a centrally disposed conductor with the other around it. Insulating property of cable conductor
1. High insulation resistance to avoid leakage current.
2. High dielectric strength to avoid electrical breakdown of the cable.
3. Good mechanical properties that is tenacity and elasticity. Good tenacity is required in the material to withstand the mechanical handling of cables.
4. Immune to attacks by acids and alkalis, over a range of temperature of about-degree to degree.
5. Non gyroscopic because the dielectric strength of any material goes very much down with moisture content. In case the insulating material is gyroscopic, it must be enclosed in a water tight covering like lead sheath.
6. It is not inflammable.
7. It should be low coefficient of thermal expansion.
8. Capacity of with outstanding high rupturing voltage.
Insulating material of cable conductor
The various insulating material used in manufacture of cables as like rubber ,VIR, paper,polyvinyl chloride, varnished cambric, polyethylene, vulcanized bitumen,cotton,enamel etc.
1. Rubber
 Rubber may be two types synthetic and natural. Natural rubber is obtained from the milky sap of tropical trees. Synthetic rubber is produced from alcohol or oil products. It dielectric strength is 30KV/mm and relative permittivity is between 2 and 3.
Rubber may be two types synthetic and natural. Natural rubber is obtained from the milky sap of tropical trees. Synthetic rubber is produced from alcohol or oil products. It dielectric strength is 30KV/mm and relative permittivity is between 2 and 3.
2. Vulcanized India rubber (VIR).
It is prepared by mixing India rubber with mineral matter such as, zinc oxide, red lead etc.
3. Impregnated paper.
It is prepared from wood pulp rags or plant fibers by a suitable chemical process. It is quit cheap, has low capacitance, high dielectric strength (30KV/mm) high insulation resistivity high thermal conductivity, better thermal with stand capability and high durability.
4. Polyvinyl chloride.
This is a synthetic compound. For obtaining this materials as a cable dielectric or sheathing. Its short form is (PVC).
5. Polythene.
Polythene is a straight chain polymer derived from ethylene. Its electrical properties are very good-low permittivity (dielectric constant),high insulation resistivity and very low power factor at all frequencies.
6. Cross-linked polythene.
Low density polythene, when vulcanized under controlled conditions, result in cross-linking of carbon atoms and the compound produced is a new material having extremely high melting point with light weight , small dimensions, low dielectric constant and food mechanical strength.
7. Varnished cambric (or empire tape).
This is a cotton cloth impregnated and coated with varnish. It has very smooth surface
8. Gutta-percha.
It is similar to rubber but it becomes soft at 65degree. it is non-gyroscopic but cannot withstand even medium voltages. It is mostly used for used for submarine cables for telephone and telegraph purposes.
9. Silk and cotton.
This is used in low voltage cables. The conductor may have a single layer or double layer covering depending upon the requirements of service.
10. Enamel insulation.
Enameled wires are also used for instrument and motor winding.